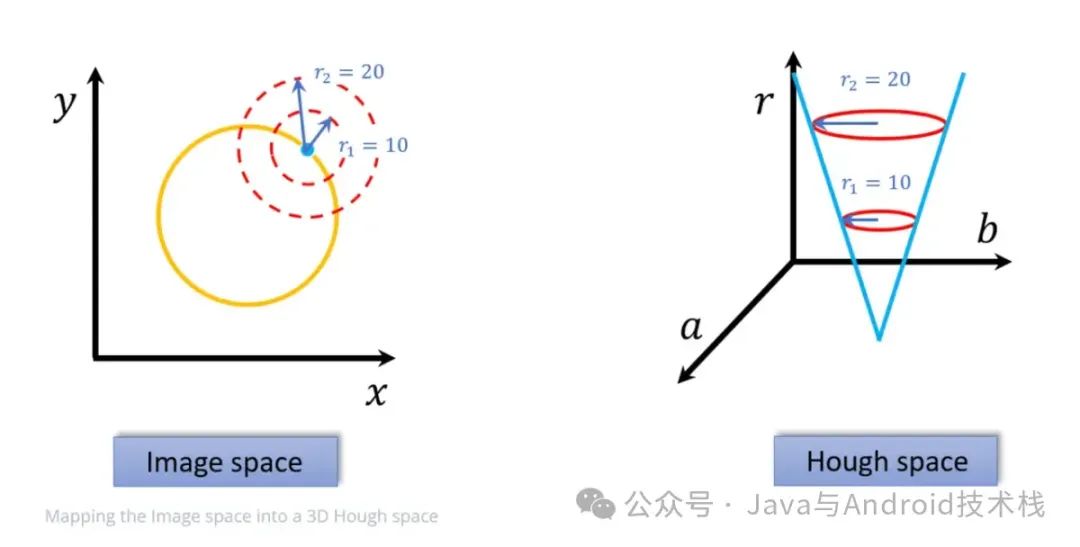
本文介绍: 以上代码仅仅是讲解介绍了图像旋转的计算及矫正原理,实际上准确度受不同图像的影响较大,不过里面使用的相关图像变换的函数值得借鉴参考学习。
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as np
import time
def Rotate(img, angle=0.0,fill=0):
"""
旋转
:param img:待旋转图像
:param angle: 旋转角度
:param fill:填充方式,默认0黑色填充
:return: img: 旋转后的图像
"""
w, h = img.shape[:2]
center = (int(w / 2), int(h / 2))
rot = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, 1.0)
img = cv2.warpAffine(img, rot, (h, w), borderValue=fill)
return img
def CalcAngle(img):
h, w = img.shape[:2]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = 0, 0, 0, 0
angle = 0
for i in range(h - 1):
if img[i][int(w / 3)] == 0 and img[i - 1][int(w / 3)] != 0:
# print("1",int(w/3),i)
x1, y1 = int(w / 3), i
if img[i][int(w * 2 / 3)] == 0 and img[i - 1][int(w * 2 / 3)] != 0:
# print("2",int(w*2/3),i)
x2, y2 = int(w * 2 / 3), i
if x1 != 0 and y1 != 0 and x2 != 0 and y2 != 0:
if x2 - x1 == 0 or y2 - y1 == 0:
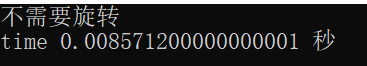
print(u"不需要旋转")
return 0
else:
length = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
angle = np.arctan(length) / 0.017453
if angle < -45:
angle = angle + 90
elif angle > 45:
angle = angle - 90
else:
pass
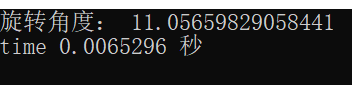
print(u"旋转角度:", angle)
return angle
starts = time.clock()
img1=cv2.imread("box.jpg",0)
# img=Rotate(img1,2,255)
ret,img=cv2.threshold(img1,200,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# cv2.imshow("0",img)
img = cv2.Canny(img, 10, 255, apertureSize=3)
angle=CalcAngle(img)
img=Rotate(img1,angle)
ends = time.clock()
print("time", ends - starts, "秒")
cv2.imwrite("00.jpg",img)
# cv2.imshow("00",img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
使用两张测试图片如下:


对于lena的图像测试结果如下:

另一张测试图片结果如下:

也可以使用下面代码进行测试:
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import time
import numpy as np
def Location(img, tmp, threshold_value=120, dilate=3, resize_multiple=16):
"""
图像定位
:param img: 输入原图
:param tmp: 定位匹配模板
:param threshold_value: 图像阈值
:param dilate: 膨胀值
:param resize_multiple:缩小倍率
:return: rect:矩形坐标点,从右上xy到右下xy,四个值
"""
h, w = img.shape[:2]
hy, wx = tmp.shape[:2]
img = cv2.resize(img, (int(w * 1 / resize_multiple), int(h * 1 / resize_multiple)), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3, 3))
img = cv2.erode(img, kernel, iterations=dilate)
w, h = img.shape[:2]
for i in range(w):
for j in range(h):
if img[i][j] >= threshold_value:
img[i][j] = 255
else:
img[i][j] = 0
res = cv2.matchTemplate(img, tmp, cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED)
min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(res)
top_left = min_loc
# bottom_right = ((top_left[0] + wx) * resize_multiple, (top_left[1] + hy) * resize_multiple)
# top_left = (top_left[0] * resize_multiple, top_left[1] * resize_multiple)
rect = [top_left[0] * resize_multiple, top_left[1] * resize_multiple, (top_left[0] + wx) * resize_multiple,
(top_left[1] + hy) * resize_multiple]
return rect
def RotateAngle(img, threshold_value=120, dilate=3,linenum=6):
"""
计算图像旋转角度
:param img: 输入图像
:param threshold_value: 阈值分割
:param dilate: 膨胀值
:return: angle: 旋转角度
"""
ret,img=cv2.threshold(img,threshold_value,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
img_w, img_h = img.shape[:2]
# kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (5, 2))
# img = cv2.erode(img, kernel, iterations=dilate)
line_widthsize = int(img_w)
line_lensize = int(img_h / linenum)
edges = cv2.Canny(img, 10, 255, apertureSize=3)
try:
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(edges, 1, np.pi / 180, line_lensize, minLineLength=int(line_widthsize / 2),
maxLineGap=line_widthsize)
for line in lines[0]:
# print("角度测量的直线坐标", line)
x1, y1, x2, y2 = line
if x2 - x1 == 0 or y2 - y1 == 0:
print(u"不需要旋转")
return 0
else:
length = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
angle = np.arctan(length) / 0.017453
if angle < -45:
angle = angle + 90
elif angle > 45:
angle = angle - 90
else:
pass
print(u"旋转角度:", angle)
return angle
except:
return 0
def Rotate(img, angle=0.0):
"""
旋转
:param img:待旋转图像
:param angle: 旋转角度
:return: img: 旋转后的图像
"""
w, h = img.shape[:2]
center = (int(w / 2), int(h / 2))
rot = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, 1.0)
img = cv2.warpAffine(img, rot, (h, w), borderValue=255)
return img
def GetObject_Location(img, tmp, threshold_value=120, dilate=3, resize_multiple=16):
"""
旋转
:param img:图像
:param tmp: 模板
:param threshold_value:阈值
:param dilate: 膨胀值
:param resize_multiple:缩放倍数
:return:
"""
rect = Location(img, tmp, threshold_value, dilate, resize_multiple)
imgout = img[rect[1]:rect[3], rect[0]:rect[2]]
angle = RotateAngle(imgout, threshold_value, dilate, resize_multiple, linenum=6)
img = Rotate(imgout, angle)
return img
def SaveTemple(img, file_name=".\data\Temple1.jpg", threshold_value=200, dilate=3, resize_multiple=16):
"""
模板生成存储
:param img: 输入图像
:param file_name: 模板保存地址
:param threshold_value: 阈值分割
:param dilate: 膨胀值
:return: img: 保存模板图片到本地
"""
h, w = img.shape[:2]
img = cv2.resize(img, (int(w * 1 / resize_multiple), int(h * 1 / resize_multiple)), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
img_w, img_h = img.shape[:2]
print(img_w, img_h)
# 创建标准模板
imgout = np.zeros((img_w + 4, img_h + 4, 1), np.uint8)
# 图像初始化白色
for i in range(img_w + 4):
for j in range(img_h + 4):
imgout[i][j] = 255
# 图像二值化
for i in range(img_w):
for j in range(img_h):
if img[i][j] >= threshold_value:
img[i][j] = 255
else:
img[i][j] = 0
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3, 3))
img = cv2.erode(img, kernel, iterations=dilate)
for i in range(img_w):
for j in range(img_h):
if img[i][j] >= threshold_value:
pass
else:
imgout[i + 2][j + 2] = 0
cv2.imwrite(file_name, imgout)
"""一次切割,根据投影切割"""
def FirstCutting(img, Cvalue, Cerode, LineNum, LineNum1):
(_, thresh) = cv2.threshold(img, Cvalue, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3, 3))
outimg = cv2.erode(thresh, kernel, iterations=Cerode)
height, width = outimg.shape[:2]
z = [0] * height
v = [0] * width
hfg = [[0 for col in range(2)] for row in range(height)]
lfg = [[0 for col1 in range(2)] for row1 in range(width)]
Box = []
linea = 0
BlackNumber = 0
for y in range(height):
for x in range(width):
cp = outimg[y][x]
if cp == 0:
linea = linea + 1
BlackNumber += 1
else:
continue
z[y] = linea
linea = 0
inline, start, lineNumber = 1, 0, 0
for i in range(0, height):
if inline == 1 and z[i] >= LineNum:
start = i
inline = 0
elif (i - start > 3) and z[i] < LineNum and inline == 0:
inline = 1
hfg[lineNumber][0] = start - 2 # 保存行的分割位置起始位置
hfg[lineNumber][1] = i + 2 # 保存行的分割终点位置
lineNumber = lineNumber + 1
lineb = 0
for p in range(0, lineNumber):
for x in range(0, width):
for y in range(hfg[p][0], hfg[p][1]):
cp1 = outimg[y][x]
if cp1 == 0:
lineb = lineb + 1
else:
continue
v[x] = lineb
lineb = 0
incol, start1, lineNumber1 = 1, 0, 0
z1 = hfg[p][0]
z2 = hfg[p][1]
for i1 in range(0, width):
if incol == 1 and v[i1] >= LineNum1:
start1 = i1
incol = 0
elif (i1 - start1 > 3) and v[i1] < LineNum1 and incol == 0:
incol = 1
lfg[lineNumber1][0] = start1 - 3
lfg[lineNumber1][1] = i1 + 3
l1 = start1 - 3
l2 = i1 + 3
tmp = [l1, z1, l2, z2]
Box.append(tmp)
lineNumber1 = lineNumber1 + 1
# outimg=cv2.rectangle(outimg,(l1,z1),(l2,z2),(0,255,0),1)
return Box, BlackNumber, outimg
def Threshold(img, threshold, KernelValue=3, KernelValue1=(1, 1)):
"""
根据阈值框选
:param img:输入待处理的图像
:param threshold:阈值
:param KernelValue:卷积核
:return:outimg:输出处理后的图像
"""
w, h = img.shape[:2]
for i in range(w):
for j in range(h):
"""通过设置阈值,来控制喷码花的程度"""
if img[i][j] >= threshold:
img[i][j] = 255
else:
img[i][j] = 0
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, KernelValue1)
outimg = cv2.erode(img, kernel, iterations=KernelValue)
outimg = cv2.dilate(outimg, kernel, iterations=KernelValue)
return outimg
"""根据投影计算出来的坐标进行数组切割"""
starts = time.clock()
img = cv2.imread("lena.jpg", 0)
# img=Rotate(img,2)
angle=RotateAngle(img,200)
print(angle)
img=Rotate(img,angle)
cv2.imwrite("00.jpg",img)
ends = time.clock()
print("time", ends - starts, "秒")
# img=cv2.imread("formal.bmp",0)
# SaveTemple(img)
lena结果如下:

美女图片测试结果:

说明:以上代码仅仅是讲解介绍了图像旋转的计算及矫正原理,实际上准确度受不同图像的影响较大,不过里面使用的相关图像变换的函数值得借鉴参考学习。
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/mzl_18353516147/article/details/135817920
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_61841.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
主题授权提示:请在后台主题设置-主题授权-激活主题的正版授权,授权购买:RiTheme官网
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。