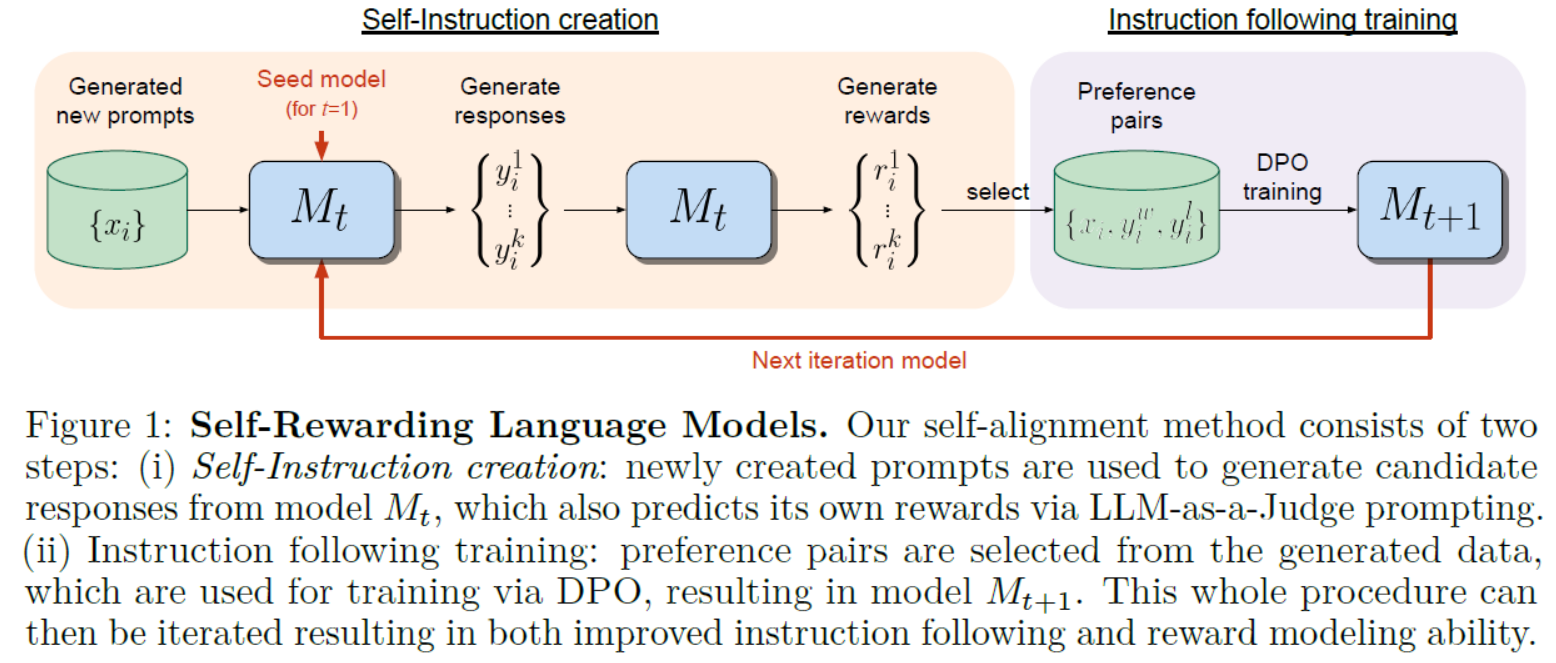
本文介绍: 【代码】机器学习:多元线性回归闭式解(Python)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class LRClosedFormSol:
def __init__(self, fit_intercept=True, normalize=True):
"""
:param fit_intercept: 是否训练bias
:param normalize: 是否标准化数据
"""
self.theta = None # 训练权重系数
self.fit_intercept = fit_intercept # 线性模型的常数项。也即偏置bias,模型中的theta0
self.normalize = normalize # 是否标准化数据
if normalize:
self.feature_mean, self.feature_std = None, None # 特征的均值,标准方差
self.mse = np.infty # 训练样本的均方误差
self.r2, self.r2_adj = 0.0, 0.0 # 判定系数和修正判定系数
self.n_samples, self.n_features = 0, 0 # 样本量和特征数
def fit(self, x_train, y_train):
"""
模型训练,根据是否标准化与是否拟合偏置项分类讨论
:param x_train: 训练样本集
:param y_train: 训练目标集
:return:
"""
if self.normalize:
self.feature_mean = np.mean(x_train, axis=0) # 按样本属性计算样本均值
self.feature_std = np.std(x_train, axis=0) + 1e-8 # 样本方差,为避免零除,添加噪声
x_train = (x_train - self.feature_mean) / self.feature_std # 标准化
if self.fit_intercept:
x_train = np.c_[x_train, np.ones_like(y_train)] # 添加一列1,即偏置项样本
# 训练模型
self._fit_closed_form_solution(x_train, y_train) # 求闭式解
def _fit_closed_form_solution(self, x_train, y_train):
"""
线性回归的闭式解,单独函数,以便后期扩充维护
:param x_train: 训练样本集
:param y_train: 训练目标集
:return:
"""
# pinv伪逆,即(A^T * A)^(-1) * A^T
self.theta = np.linalg.pinv(x_train).dot(y_train) # 非正则化
# xtx = np.dot(x_train.T, x_train) + 0.01 * np.eye(x_train.shape[1]) # 按公式书写
# self.theta = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(xtx), x_train.T).dot(y_train)
def get_params(self):
"""
返回线性模型训练的系数
:return:
"""
if self.fit_intercept: # 存在偏置项
weight, bias = self.theta[:-1], self.theta[-1]
else:
weight, bias = self.theta, np.array([0])
if self.normalize: # 标准化后的系数
weight = weight / self.feature_std.reshape(-1) # 还原模型系数
bias = bias - weight.T.dot(self.feature_mean.reshape(-1))
return np.r_[weight.reshape(-1), bias.reshape(-1)]
def predict(self, x_test):
"""
测试数据预测,x_test:待预测样本集,不包括偏置项1
:param x_test:
:return:
"""
try:
self.n_samples, self.n_features = x_test.shape[0], x_test.shape[1]
except IndexError:
self.n_samples, self.n_features = x_test.shape[0], 1 # 测试样本数和特征数
if self.normalize:
x_test = (x_test - self.feature_mean) / self.feature_std # 测试数据标准化
if self.fit_intercept:
x_test = np.c_[x_test, np.ones(shape=x_test.shape[0])] # 存在偏置项,添加一列1
return x_test.dot(self.theta)
def cal_mse_r2(self, y_pred, y_test):
"""
计算均方误差,计算拟合优度的判定系数R方和修正判定系数
:param y_pred: 模型预测目标真值
:param y_test: 测试目标真值
:return:
"""
self.mse = ((y_test - y_pred) ** 2).mean() # 均方误差
# 计算测试样本的判定系数和修正判定系数
self.r2 = 1 - ((y_test - y_pred) ** 2).sum() / ((y_test - y_test.mean()) ** 2).sum()
self.r2_adj = 1 - (1 - self.r2) * (self.n_samples - 1) / (self.n_samples - self.n_features - 1)
return self.mse, self.r2, self.r2_adj
def plt_predict(self, y_pred, y_test, is_show=True, is_sort=True):
"""
绘制预测值与真实值对比图
:return:
"""
if self.mse is np.infty:
self.cal_mse_r2(y_pred, y_test)
if is_show:
plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5))
if is_sort:
idx = np.argsort(y_test)
plt.plot(y_pred[idx], "r:", lw=1.5, label="Predictive Val")
plt.plot(y_test[idx], "k--", lw=1.5, label="Test True Val")
else:
plt.plot(y_pred, "r:", lw=1.5, label="Predictive Val")
plt.plot(y_test, "k--", lw=1.5, label="Test True Val")
plt.xlabel("Test sample observation serial number", fontdict={"fontsize": 12})
plt.ylabel("Predicted sample value", fontdict={"fontsize": 12})
plt.title("The predictive values of test samples n MSE = %.5e, R2 = %.5f, R2_adj = %.5f"
% (self.mse, self.r2, self.r2_adj), fontdict={"fontsize": 14})
plt.legend(frameon=False)
plt.grid(ls=":")
if is_show:
plt.show()
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score, mean_squared_error
housing = fetch_california_housing()
X, y = housing.data, housing.target # 获取样本数据和目标数据
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test =
train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=1, shuffle=True)
lgcfs_obj = LRClosedFormSol(normalize=True, fit_intercept=True)
lgcfs_obj.fit(X_train, y_train)
theta = lgcfs_obj.get_params() # 获得模型系数
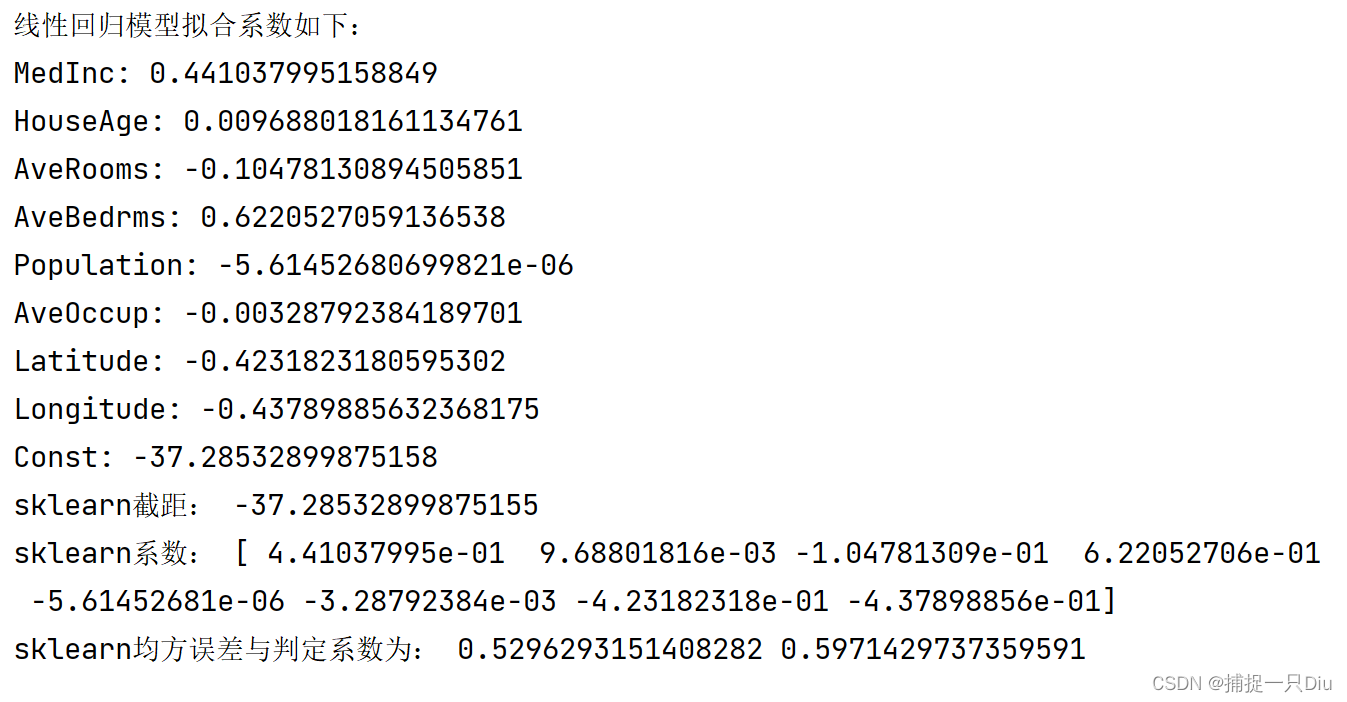
print("线性回归模型拟合系数如下:")
for i, fn in enumerate(housing.feature_names):
print(fn + ":", theta[i])
print("Const:", theta[-1])
# 模型预测,即针对测试样本进行预测
y_pred = lgcfs_obj.predict(X_test)
lgcfs_obj.plt_predict(y_pred, y_test, is_sort=True)
# 采用sklearn库函数进行线性回归和预测
lr = LinearRegression().fit(X_train, y_train)
print("sklearn截距:", lr.intercept_) # 打印截距
print("sklearn系数:", lr.coef_) # 打印模型系数
y_test_predict = lr.predict(X_test)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_test_predict)
r2 = r2_score(y_test, y_test_predict)
print("sklearn均方误差与判定系数为:", mse, r2)

原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/2302_78896863/article/details/135839224
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_62075.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
主题授权提示:请在后台主题设置-主题授权-激活主题的正版授权,授权购买:RiTheme官网
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。