一、什么是Vuex
Vuex就是一个vue的状态(数据)管理工具,是vue项目实现大范围数据共享的技术方案。能够方便、高效的实现组件之间的数据共享。
Vuex的好处:
(1)数据的存储一步到位,不需要层层传递
(2)数据的流动十分清晰
(3)存储在Vuex中的数据都是响应式的(数据更新后,使用数据的组件也会自动更新)
适合存储到Vuex中的数据—-需要共享的数据
Vuex的使用场景:
频繁、大范围的数据共享。
(1)某个状态在很多个组件中使用
(2)多个组件共同维护一份数据

二、Vuex的安装及配置
1、执行以下命令,安装Vuex
注:我的项目是vue2的项目,所以安装的是3.6.2版本的vuex
npm i vuex@3.6.22、新建src/store/index.js,专门存放vuex
在src目录下新建store文件夹,并在store文件夹下新建index.js文件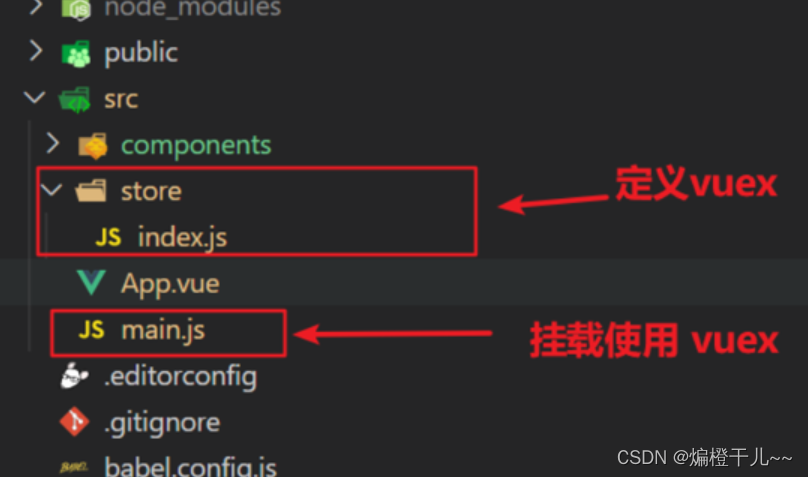
3、创建仓库
index.js 内容如下:
// 导入 vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 导入 vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// vuex也是vue的插件, 需要use一下, 进行插件的安装初始化
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建仓库实例对象 store
const store = new Vuex.Store()
// 导出仓库对象
export default store4、挂载到main.js中
在main.js中导入,并挂载到Vue示例上
main.js中的内容如下:
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from './store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
store
}).$mount('#app')4、测试仓库是否创建成功
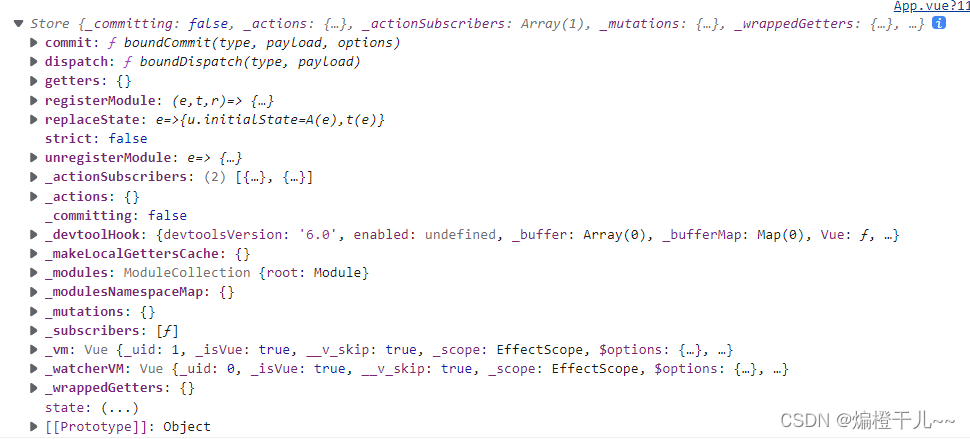
在App.vue中,打印store对象,控制台查看结果
created(){
console.log(this.$store)
}若控制台输出如下内容,则代表创建仓库成功
三、state的基础使用
state作用:state属性的值是一个对象,用于存储全局共享的数据。
1、存储数据
在store/index.js中添加如下内容:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
//这里配置vuex
// state 用于存储数据(存储状态)(Vuex状态管理)
state: {
age: 18,
name: 'Tom',
list: [
{ id: 1, name: 'John', isDone: true },
{ id: 2, name: 'Juliy', isDone: true },
{ id: 2, name: 'Lily', isDone: true },
],
},
})2、vue页面中使用
<div>
组件1
<p>{{ $store.state.name + '--' + $store.state.age }}</p>
</div>3、js中使用
import store from "@/store"
console.log(store.state.age)4、 结果

5、严格模式
开启严格模式,防止在组件中直接修改state数据,开启后,若直接修改state数据,会报错
开启方法:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
//这里配置vuex
// 开启严格模式,防止在组件中直接修改state数据
strict: true,
})四、mutations的基础使用
mutations作用: 修改state数据,且是修改state数据的唯一途径
1、定义方法
在store/index.js中添加如下内容:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
mutations: {
updateAge (state, newAge) {
state.age = newAge
},
},
})2、vue页面中使用
<button @click="$store.commit('updateAge', 20)">更新年龄</button>3、结果
页面点击更新年龄按钮,页面中年龄会发生变化


五、actions的基础使用
mutations是同步更新数据 (便于监测数据的变化, 更新视图等, 方便于调试工具查看变化),
actions则负责进行异步操作。
1、定义方法
在store/index.js中添加如下内容:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// mutations里面放同步方法
mutations: {
updateAge (state, newAge) {
state.age = newAge
},
},
// actions里面放异步方法
actions: {
updateAgeAfter3s (store, newAge) {
setTimeout(() => {
// 只有mutations可以修改数据,所以这里调用mutations的方法
store.commit('updateAge', newAge)
}, 3000)
},
},
})2、vue页面中的使用
<button @click="$store.dispatch('updateAgeAfter3s', 30)">3s后更新年龄</button>3、结果
页面点击3s后更新年龄按钮,页面中年龄会在3s后发生变化


六、getters的基础使用
getters作用:getters是Vuex中的计算属性(和组件中的计算属性意义一样,但不支持set修改)
1、定义方法
在store/index.js中添加如下内容:
// 为了方便获取state中的数据,vuex会给每个计算属性的方法,传递一个state参数
getters: {
ageComputed (state) {
return state.age * 2
},
},2、vue页面中使用
<p>{{ $store.getters.ageComputed }}</p>3、结果

七、借助辅助方法使用state和getters
mapState和mapGetters是辅助函数,帮助我们把store中的数据映射到组件的计算属性中, 它属于一种方便的用法。
store/index.js中的内容不变,还是上方的内容,只有vue页面的使用需要修改。
1、 导入mapState和mapGetters
import { mapState, mapGetters } from 'vuex'2、利用展开运算符映射到computed计算属性中
computed: {
...mapState(['age', 'name']),
...mapGetters(['ageComputed']),
},注:若state中字段名与data中字段名重复,可采用以下方法引入
...mapState({ ages: 'age', uname: 'name' })3、vue页面中使用
<p>{{ ages + '---' + uname }}</p>
<p>{{ ageComputed }}</p>4、结果

八、借助辅助方法使用mutations和actions
mapMutations和mapActions,把位于mutations和actions中的方法提取了出来,我们可以将它导入到methods中方便使用。
1、导入mapMutations和mapActions
import { mapMutations, mapActions } from 'vuex'2、利用展开运算符映射到methods方法中
methods: {
...mapMutations(['updateAge']),
...mapActions(['updateAgeAfter3s']),
},3、vue页面中使用
<button @click="updateAge(22)">更新年龄</button>
<br />
<button @click="updateAgeAfter3s(24)">3s后更新年龄</button>4、结果

九、vuex模块化—modules
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。
即,如果把所有的状态都放在state中,当项目变得越来越大的时候,Vuex会变得越来越难以维护。
由此,又有了Vuex的模块化。

1、模块定义
在store文件夹下,新建modules文件夹,在modules文件夹中新建user.js和todo.js文件,文件目录如下:

user.js 的内容如下:
// 存储用户相关数据
export default {
// 开启命名空间,必须的操作
namespaced: true,
// state 用于存储数据(存储状态)(Vuex状态管理)
state: {
age: 18,
name: 'Tom',
},
// mutations是修改state数据的唯一途径
// 所有方法不支持一步更新,只支持同步方法
mutations: {
updateAge (state, newAge) {
state.age = newAge
},
},
// actions里面放异步方法
actions: {
updateAgeAfter3s (store, newAge) {
setTimeout(() => {
// 只有mutations可以修改数据,所以这里调用mutations的方法
store.commit('updateAge', newAge)
}, 3000)
},
},
// getters是Vuex中的计算属性(和组件中的计算属性意义一样,但不支持set修改)
// 为了方便获取state中的数据,vuex会给每个计算属性的方法,传递一个state参数
getters: {
ageComputed (state) {
return state.age * 2
},
},
}
todo.js的内容如下:
// 存储列表相关数据
export default {
// 开启命名空间,必须的操作
namespaced: true,
// state 用于存储数据(存储状态)(Vuex状态管理)
state: {
list: [
{ id: 1, name: 'John', isDone: true },
{ id: 2, name: 'Juliy', isDone: true },
{ id: 3, name: 'Lily', isDone: true },
],
},
}
2、在index.js中导入并注册modules模块
store/index.js 内容如下:
// 导入 vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 导入 vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 导入小模块
import user from './modules/user'
import todo from './modules/todo'
// vuex也是vue的插件, 需要use一下, 进行插件的安装初始化
// 将vuex注册为插件
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建仓库 store
// 创建store实例对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 这里配置vuex
// 开启严格模式,防止在组件中直接修改state数据
strict: true,
// modules模块注册
modules: {
user,
todo,
},
})
// 导出仓库/对象
export default store
3、vue页面中直接使用
<template>
<div>
组件1
<p>{{ $store.state.user.name + '--' + $store.state.user.age }}</p>
<p>{{ $store.getters['user/ageComputed'] }}</p>
<button @click="$store.commit('user/updateAge', 20)">更新年龄</button>
<br />
<button @click="$store.dispatch('user/updateAgeAfter3s', 30)">3s后更新年龄</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {}
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped></style>4、利用辅助方法调用
<template>
<div>
组件2
<p>{{ age + '---' + name }}</p>
<!-- <p>{{ ages + '---' + uname }}</p> -->
<p>{{ ageComputed }}</p>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in list" :key="item.id">{{ item.name }}</li>
</ul>
<br />
<button @click="updateAge(22)">更新年龄</button>
<br />
<button @click="updateAgeAfter3s(24)">3s后更新年龄</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
...mapState('user', ['age', 'name']),
...mapState('todo', ['list']),
// 若state中字段名与data中字段名重复,可采用以下方法引入
// ...mapState({ ages: 'age', uname: 'name' }),
...mapGetters('user', ['ageComputed']),
},
methods: {
...mapMutations(['user/updateAge']),
...mapActions(['user/updateAgeAfter3s']),
},
}
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped></style>
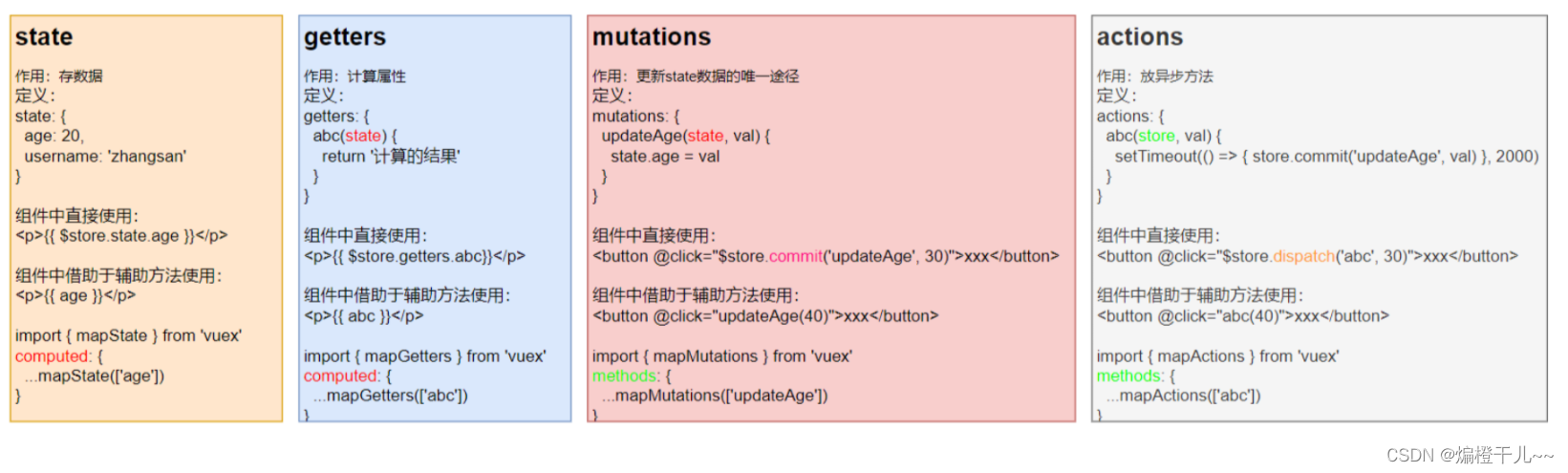
十、state、getters、mutations、actions的对比
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_34896766/article/details/135838704
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_62499.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!