什么是IntervalMatch
IntervalMatch 前缀用于创建表格以便将离散数值与一个或多个数值间隔进行匹配,并且任选匹配一个或多个额外关键值。
语法:
IntervalMatch (matchfield)(loadstatement | selectstatement )
IntervalMatch (matchfield,keyfield1 [ , keyfield2, … keyfield5 ] ) (loadstatement | selectstatement )
IntervalMatch 前缀必须置于加载时间间隔的 LOAD 或 SELECT 语句之前。在使用此语句和 IntervalMatch 前缀之前,包含离散数据点的字段(以下所示的 Time)必须已经加载到 Qlik Sense。此前缀不会从数据库表格中读取此字段。此前缀将加载的时间间隔表格转换为包含其他列(离散数值数据点)的表格。另外其扩展了记录数,以使新表格对离散数据点、时间间隔和关键字段值的每个可能组合都有一条记录。
时间间隔可以重叠,离散值可以链接所有匹配的时间间隔。
使用关键字段扩展 IntervalMatch 前缀时,可用于创建既能将离散数值和一个或多个数值时间间隔匹配的表格,同时又能匹配一个或多个额外关键字段值。
要避免未定义的时间间隔限值遭到忽略,可能必须让 NULL 可以映射到构成时间间隔下限或上限的其他字段。这可通过 NullAsValue 语句或显式测试来处理,显式测试可在任何离散数值数据点前后使用数值很好地替代 NULL。
参数
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| matchfield | 一个字段,包含链接至时间间隔的离散数值。 |
| keyfield | 一个字段,包含转换中匹配的额外属性。 |
| loadstatementorselectstatement | 必会生成一个表格,其中第一个字段包含每个时间间隔的下半部限制,第二个字段包含每个时间间隔的上半部限制,如果使用关键字匹配,则第三个及此后的任何字段包含显示于 IntervalMatch 语句中的关键字段值。时间间隔总是封闭区间,即间隔的端点包括在时间间隔之中。非数值限值会导致时间间隔遭到忽略(未定义)。 |
Show Me The Code
示例 1:
在以下两个表格中,第一个表格列出了众多离散事件,第二个表格定义了不同订单生产的开始时间和结束时间。借助 IntervalMatch 前缀,可以逻辑连接两个表格,从而找出哪些订单受到干扰的影响,哪些订单依据哪次轮班处理。
EventLog:
LOAD * Inline [
Time, Event, Comment
00:00, 0, Start of shift 1
01:18, 1, Line stop
02:23, 2, Line restart 50%
04:15, 3, Line speed 100%
08:00, 4, Start of shift 2
11:43, 5, End of production
];
OrderLog:
LOAD * INLINE [
Start, End, Order
01:00, 03:35, A
02:30, 07:58, B
03:04, 10:27, C
07:23, 11:43, D
];
//Link the field Time to the time intervals defined by the fields Start and End.
Inner Join IntervalMatch ( Time )
LOAD Start, End
Resident OrderLog;
从DataModel来看,会把匹配上的关联起来,在OrderLog中展示7条记录,但是你任然可以通过建table的方式显示以下所有字段,并把第八条空值记录显示出来。
表格 OrderLog 现在包含额外一列:Time。记录的数量也可以扩展。
| Time | Start | End | Order |
|---|---|---|---|
|
00:00 |
– | – | – |
| 01:18 | 01:00 | 03:35 | A |
| 02:23 | 01:00 | 03:35 | A |
| 04:15 | 02:30 | 07:58 | B |
| 04:15 | 03:04 | 10:27 | C |
| 08:00 | 03:04 | 10:27 | C |
| 08:00 | 07:23 | 11:43 | D |
| 11:43 | 07:23 |
11:43 |
D |
示例 2: (使用 keyfield)
与上述示例相同,添加 ProductionLine 作为关键字段。
EventLog:
LOAD * Inline [
Time, Event, Comment, ProductionLine
00:00, 0, Start of shift 1, P1
01:00, 0, Start of shift 1, P2
01:18, 1, Line stop, P1
02:23, 2, Line restart 50%, P1
04:15, 3, Line speed 100%, P1
08:00, 4, Start of shift 2, P1
09:00, 4, Start of shift 2, P2
11:43, 5, End of production, P1
11:43, 5, End of production, P2
];
OrderLog:
LOAD * INLINE [
Start, End, Order, ProductionLine
01:00, 03:35, A, P1
02:30, 07:58, B, P1
03:04, 10:27, C, P1
07:23, 11:43, D, P2
];
//Link the field Time to the time intervals defined by the fields Start and End and match the values
// to the key ProductionLine.
Inner Join
IntervalMatch ( Time, ProductionLine )
LOAD Start, End, ProductionLine
Resident OrderLog;补充:从data model来看,其实已经把Time和ProductionLine建立起关系了,这就是IntervalMatch的作用,成立中间表把两个表Match起来。
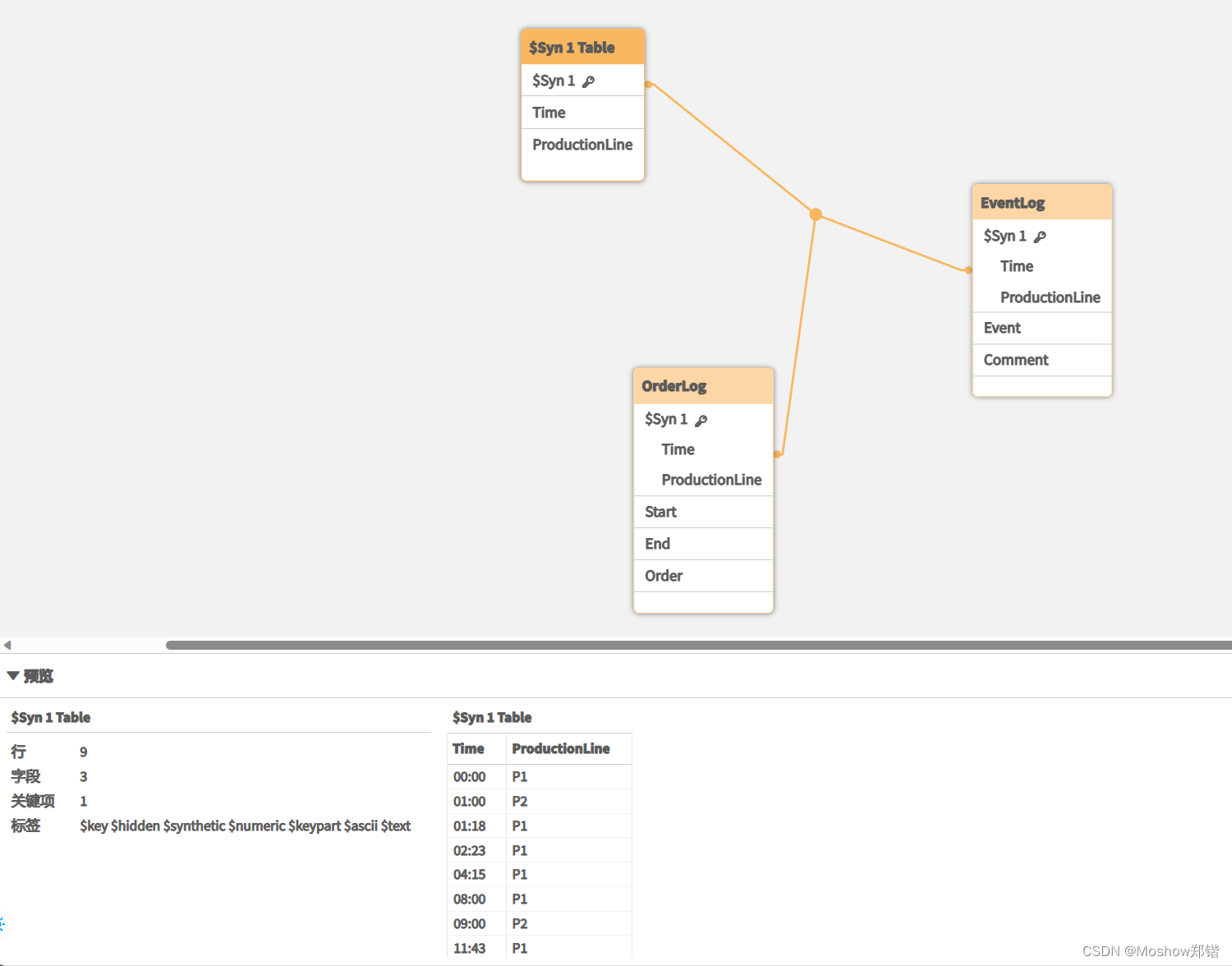
现在可以按照以下方式创建表格框:
| ProductionLine | Time | Event | Comment | Order | Start | End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 |
00:00 |
0 | Start of shift 1 | – | – | – |
| P2 | 01:00 | 0 | Start of shift 1 | – | – | – |
| P1 | 01:18 | 1 | Line stop | A | 01:00 | 03:35 |
| P1 | 02:23 | 2 | Line restart 50% | A | 01:00 | 03:35 |
| P1 | 04:15 | 3 | Line speed 100% | B | 02:30 | 07:58 |
| P1 | 04:15 | 3 | Line speed 100% | C | 03:04 | 10:27 |
| P1 | 08:00 | 4 | Start of shift 2 | C | 03:04 | 10:27 |
| P2 | 09:00 | 4 | Start of shift 2 | D | 07:23 | 11:43 |
| P1 | 11:43 | 5 | End of production | – | – | – |
| P2 | 11:43 | 5 | End of production | D | 07:23 | 11:43 |
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/moshowgame/article/details/135902958
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_64129.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!