
虽然一些动物物种存在于通常的雄性或雌性性别之外,但大多数物种实质上是雄性或雌性。虽然许多物种在出生时的性别比例为1:1,但其他物种的性别比例并不均匀。这被称为适应性性别比例的变化。例如,美洲短吻鳄孵化卵的巢穴的温度会影响其出生时的
性别比例。
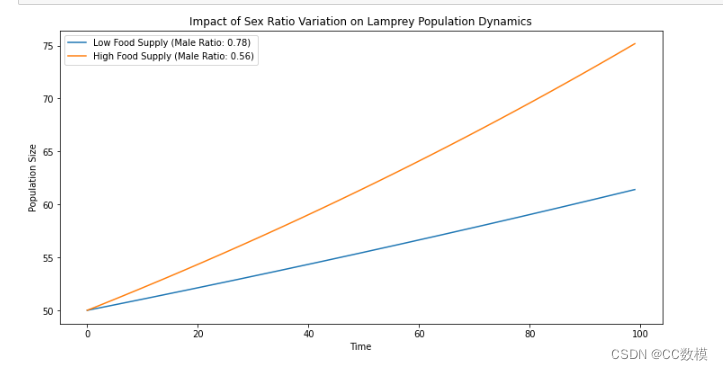
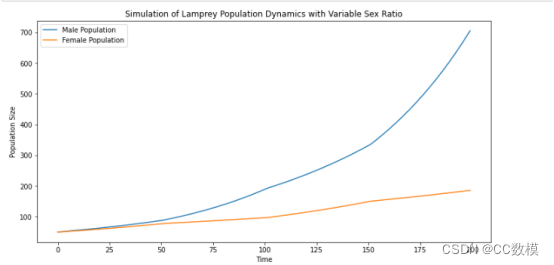
七鳃鳗的作用是复杂的。在一些湖泊栖息地,它们被视为对生态系统有重大影响的寄生虫,而七鳃鳗在世界的一些地区也是食物来源,如斯堪的纳维亚,波罗的海,以及太平洋西北部的一些土著民族的北美。海洋七鳃鳗的性别比例可能因外部环境而异。海七鳃鳗变成雄性或雌性取决于它们在幼虫阶段的生长速度。这些幼虫的生长速度受到食物供应的影响。在食物供应率较低的环境中,增长率将会较低,雄性的比例可达到约占人口的78%。在食物更容易获得的环境中
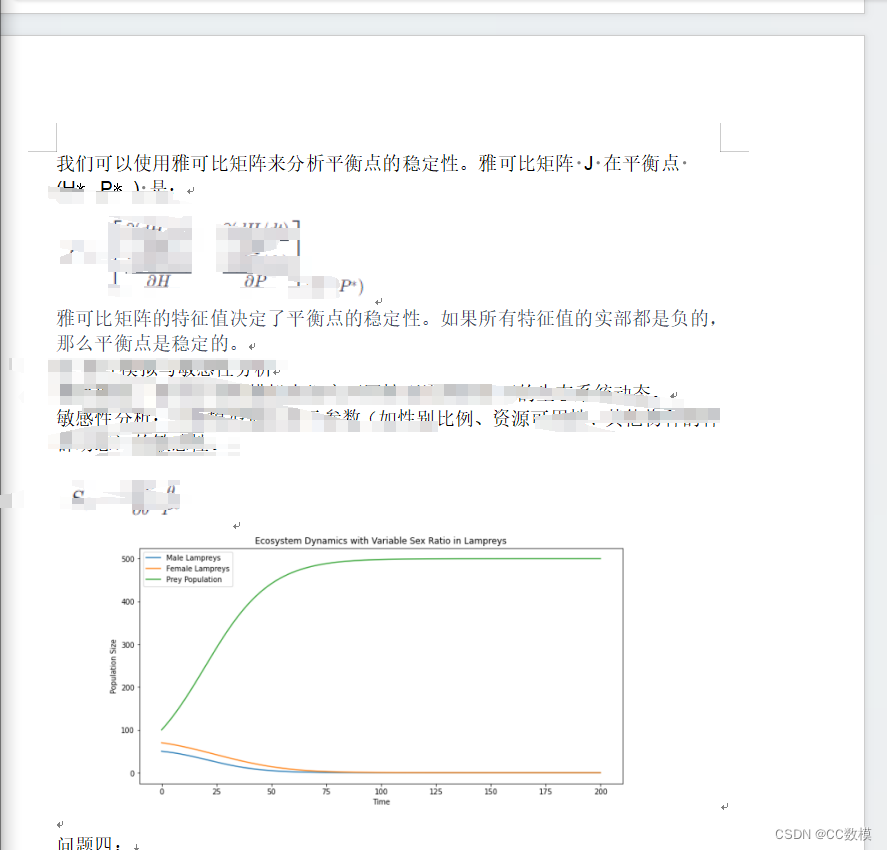
,男性的比例约占人口的56%。我们关注的问题是性别比例及其对当地条件的依赖性,特别是对海洋七鳃鳗。海七鳃鳗生活在湖泊或海洋的栖息地,并迁移到河流上产卵。其任务是检查一个物种根据资源可用性而改变其性别比例的能力的优缺点。您的团队应该开发并检查一个模型,以深入了解生态系统中由此产生的相互作用。(While some animal species exist outside of the usual male or female sexes, most species are substantially either male or female. Although many species exhibit a 1:1 sex ratio at birth, other species deviate from an even sex ratio. This is called adaptive sex ratio variation. For example, the temperature of the nest incubating eggs of the American alligator influences the sex ratios at birth. The role of lampreys is complex. In some lake habitats, they are seen as parasites with a significant impact on the ecosystem, whereas lampreys arealso a food source in some regions of the world, such as Scandinavia, the Baltics, and for some Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest in North America. The sex ratio of sea lampreys can vary based on external circumstances. Sea lampreys become male or female depending on how quickly they grow during the larval stage. These larval growth rates are influenced by the availability of food. In environments where food availability is low, growth rates will be lower, and the percentage of males can reach approximately 78% of the population. In environments where food is more readily available, the percentage of males has been observed to be approximately 56% of the population. We focus on the question of sex ratios and their dependence on local conditions, specifically for
sea lampreys. Sea lampreys live in lake or sea habitats and migrate up rivers to spawn. The task is to examine the advantages and disadvantages of the ability for a species to alter its sex ratio depending on resource availability. Your team should develop and examine a model to provide insights into the resulting interactions in an ecosystem.)













![[软件工具]文档页数统计工具软件pdf统计页数word统计页数ppt统计页数图文打印店快速报价工具](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/09dfbaff3e9a47a9a551dd65fef5d482.jpeg)