目录
一、各数据类型的基础知识点
1.1 数值类型
int 代表整数(hive常用bigint): float代表小数,double代表双精度,double比float精度更高,小数位更多。
整数
- int
有符号(signed)的和无符号(unsigned)的。有符号的取值区间为-2147483648~2147483647,无符号的取值区间为0~ 4294967295。宽度最多为11个数字 -int(11)
- tinyint
有符号和无符号的。有符号的取值范围是-128~127, 无符号的取值范围是0~255。 宽度最多为4个数字 -tinyint(4)
- smallint
有符号和无符号的。有符号的取值范围是-32767~32767 ,无符号的取值范围是0~65535。 宽度最多为4个数字 -tinyint(4)
- mediumint
有符号和无符号的。有符号的取值范围是-8388608~8388607 ,无符号的取值范围是0~16777215。 宽度最多为9个数字 -mediumint(9)
- bigint(常用)
有符号的和无符号的。宽度最多为20个数字-bigint(20)
小数
-
float
代表小数,默认是(10,2)
-
double(常用)
代表双精度,默认是(16,4)
-
decimal(针对高精度)
比float精度更高,小数位更多,默认为(16,4)
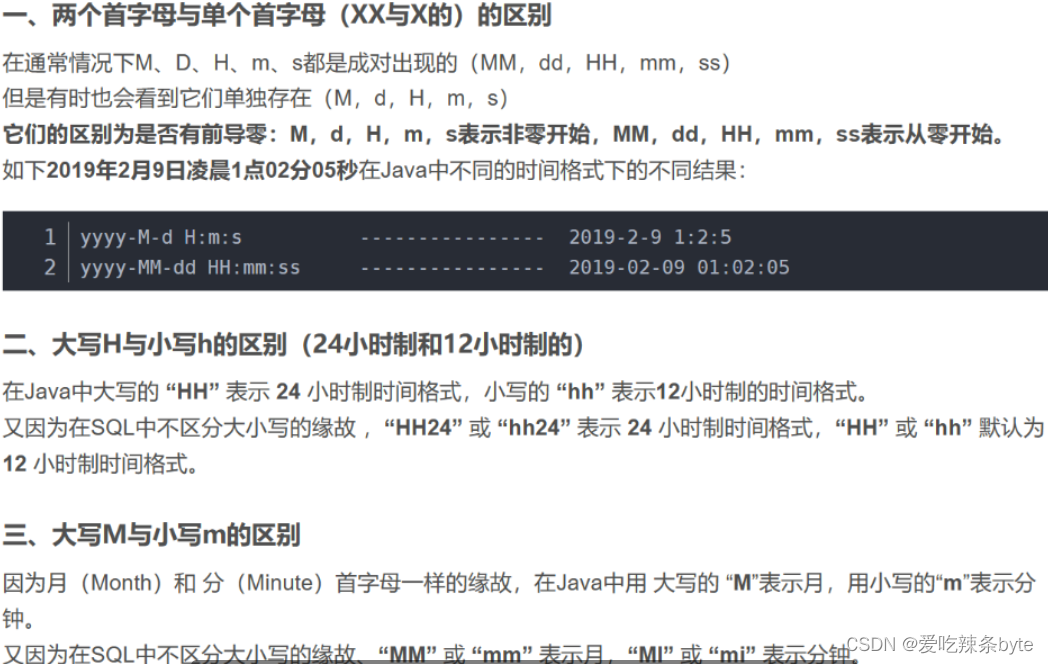
1.2 日期类型
-
date
代表 YYYY-MM-DD格式,例如:1989-12-31
-
datetime
代表 YYYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS 格式,例如:1989-12-31 15:30:00
-
timestamp
代表 时间戳,例如:1989年12月31日下午15:30,在数据库中存储为:19891231153000
-
time
代表 HH:MM:SS格式
-
year
以2位或4位格式存储年份值
- 补充
1.3 字符串类型
-
char
固定长度字符串(可以是汉字或字母),长度是1-255。如果内容小于指定长度,右边填充空格,如果不指定长度,默认是1。
-
varchar / varchar2
可变字符串,长度取值是1-255。创建表使用该类型时必须指定长度。
-
blob /text
最大长度65535,用于存储二进制大数据,如图片,无法指定长度。两者区别:blob类型对于大小写比较敏感。
-
tinyblob / tinytext
最大长度是255,不能指定长度。
-
mediumblob / mediumtext
最大长度是16777215字符。
-
longblob / longtext
最大长度是429496295字符。
-
string(常用)
二、Hive中的常用函数
2.1 数值转换函数
round
取整
- 语法:round(double a)
- 返回值:bigint
- 说明:返回double类型的整数值部分(遵循四舍五入)
- 举例:select round(4.1578 ) –> 4
精度取整函数
- 语法:round(double a, int b)
- 返回值:double
- 说明:返回指定精度的double类型
- 举例:select round(4.1578 , 2) –> 4.16
floor(向下取整函数)
- 语法:floor(double a)
- 返回值:bigint
- 说明:返回等于或者小于该double变量的最大整数
- 举例:select floor(34.12) –> 34
ceil(向上取整函数)
- 语法:ceil(double a)
- 返回值:bigint
- 说明:返回大于或者等于该double变量的最小的整数
- 举例:select ceil(34.12) –> 35
abs(绝对值函数)
- 语法:abs(double a ) 、abs(int a)
- 返回值:double 、int
- 说明:返回数值a的绝对值
- 举例:select abs( – 3.9) –> 3.9
rand(取随机数函数)
- 语法:rand() 、rand(int n)
- 返回值:double
- 说明:rand(): 返回[0,1]范围内的随机数;
- 举例:select rand()
2.2 日期函数
from_unixtime(时间戳转日期函数)
- 语法:from_unixtime(bigint unixtime , string format)
- 返回值:double
- 说明:将unix时间戳转换到当前时区 的时间格式 ( 从1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC 到指定时间相差的秒数 )
- 举例:select from_unixtime(1323308943,’yyyyMMdd’) –> 20111208
unix_timestamp(日期转时间戳函数)
- 语法:unix_timestamp(string date) 、unix_timestamp(string date,string pattern)
- 返回值:bigint
- 说明:将格式为”yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss”的日期 转换成 unix的时间戳。如果转换失败,则返回值为0;
举例:
select unix_timestamp('2024-02-01 22:17:23') --> 1706825843
select unix_timestamp('20240201 20:17:11','yyyyMMdd HH:mm:ss') --> 1706825843to_date(日期时间转日期函数)
- 语法:to_date(string timestamp)
- 返回值:string
- 说明:返回日期时间字段中的日期部分
- 举例:select to_date(‘2024-02-01 22:17:23’) —> 2024-02-01
year(日期转年函数)
- 语法:year(string date)
- 返回值:int
- 说明:返回日期中的年份
- 举例:select year(‘2024-02-01 22:17:23’) —> 2024
month(日期转月函数)
- 语法:month(string date)
- 返回值:int
- 说明:返回日期中的月份
- 举例:select month(‘2024-02-01 22:17:23’) —> 2
day(日期转天函数)
- 语法:day(string date)
- 返回值:int
- 说明:返回日期中的天
- 举例:select day(‘2024-02-01 22:17:23’ ) —> 1
hour(日期转小时函数)
- 语法:hour(string date)
- 返回值:int
- 说明:返回日期中的小时
- 举例:select hour(‘2024-02-01 22:17:23’) —>22
minute(日期转分钟函数)
- 语法:minute(string date)
- 返回值:int
- 说明:返回日期中的分钟
- 举例:select minute(‘2024-02-01 22:17:23’) —> 17
second(日期转秒函数)
- 语法:second(string date)
- 返回值:int
- 说明:返回日期中的秒
- 举例:select (‘2024-02-01 22:17:23’) —> 23
weekofyear(日期转周函数)
- 语法:weekofyear(string date)
- 返回值:int
- 说明:返回该日期在当年的周数
- 举例:select weekofyear (‘2024-02-01 22:17:23’) —>5
datediff(日期比较函数)
- 语法:datediff(string enddate,string startdate)
- 返回值:int
- 说明:返回 结束日期减去开始日期的天数
- 举例:select datediff (‘2024-02-01′,’2024-01-28’) —> 4
date_add(日期增加函数)
- 语法:date_add(string startdate , int days)
- 返回值:string
- 说明:返回 开始日期startdate 加上days天后的日期
- 举例:select date_add(‘2024-02-01’,10) —> 2024-02-11
date_sub
- 语法:date_sub(string startdate,int days)
- 返回值:string
- 说明:返回 开始日期startdate 减去days天后的日期
- 举例:select date_sub(‘2024-02-01’,3) —>2024-01-29
months_between
- 语法:months_between(string enddate,string startdate)
- 返回值:double
- 说明:返回 结束日期减去开始日期的月份数
举例:
select months_between('2024-02-01','2024-01-01') --> 1
select months_between('2024-02-01','2024-01-11') --> 0.67741935 2.3 条件函数
if
- 语法:if(boolean testCondition, T valueTrue, T valueFalseOrNull)
- 返回值:T
- 说明:当条件testCondition为TRUE时,返回valueTrue;否则返回valueFalseOrNull
- 举例:select if(1=2,100,200) –> 200
coalesce() /nvl(非空函数)
- 语法:coalesce(T v1,T v2 …)
- 返回值:T
- 说明:返回参数中的第一个非空值,如果所有值都为null,那么直接返回null
- 举例:select coalesce(null,’100′,’50’) –> 100
- 两者区别
1.coalesce
coalesce函数语法是:coalesce(表达式1,表达式2.....表达式n); coalesce函数的返回结果是第一个非空表达式,如果全是空,则返回空。
coalesce函数的处理参数个数没有限制,使用时需要注意:对处理参数的数据类型有严格要求,所有表达式值是同一类型(转换成同一类型也可)。
2.nvl
nvl函数语法是:nvl(默认值,表达式); 如果默认值不为空返回默认值,如果默认值是空,则返回 表达式,如果两者都为空则返回空。
nvl函数的处理参数个数有限,只能传两个参数。使用时需注意:“默认值”,“表达式”的值的数据类型没有要求,可相同也可不同。case when
- 语法:case column when vlaue1 then result1
when vlaue1 then result2
else esult3
end as column1 - 返回值:T
- 说明:如果column等于 vlaue1,那么返回result1 ; 如果column等于 vlaue2,那么返回result2;否则返回result3
举例:
select case 100 when 500 then 'false'
when 100 then 'true'
else '?' end ; 最终的输出结果是:true2.4 字符串函数
length(字符串长度函数)
- 语法:length(string A)
- 返回值:int
- 说明:返回字符串的长度
- 举例:select length(‘sghanan’) ; —> 7
reverse(字符串反转函数)
- 语法:reverse(string A)
- 返回值:string
- 说明:返回字符串A的反转结果
- 举例:select reverse(‘sghanxh’) ; —> hxnahgs
concat(字符串拼接函数)
- 语法:concat(string A ,string B…….)
- 返回值:string
- 说明:返回字符串拼接后的结果,支持输入任意个数的字符串
- 举例:select concat(‘ad’,’cv’,’op’) ;—> adcvop
concat_ws(带分隔符的字符串连接函数)
- 语法:concat_ws(string SEP, string A ,string B…….)
- 返回值:string
- 说明:返回输入字符串连接后的结果,SEP表示各个字符串的分隔符
- 举例:select concat_ws(‘|’,’ad’,’cv’,’op’) ;—> ad|cv|op
substr / substring(字符串截取函数)
- 语法:subtr( string A , int start) , substring( string A , int start )
start 代表的是:截取起始的位置(从1 开始计数)
- 返回值:string
- 说明:截取从start 位置到结尾的字符串
- 举例:select substr( ‘abcde’ ,3) –> cde
select substr( ‘abcde’ ,-1) –> e
upper (字符串转大写函数)
- 语法:upper(string A)
- 返回值:string
- 说明:返回字符串A的大写格式
- 举例:select upper(‘absSedF’) —-> ABSSEDF
lower (字符串转小写函数)
- 语法:lower(string A)
- 返回值:string
- 说明:去除字符串两边的空格
- 举例:select lower(‘absSedF’) —-> abssedf
trim(去空格函数)
- 语法:trim(string A)
- 返回值:string
- 说明:返回字符串A的小写格式
- 举例:select trim(‘ absSedF ‘) —-> absSedF
select length(‘ absSedF ‘) —> 10
regexp_replace(正则表达式的替换函数)
- 语法:regexp_replace(string A, string B, string C)
- 返回值:string
- 说明:将字符串A中符合java正则表达式的B替换成C;注意:有些情况下要使用转义字符;
举例:
select regexp_replace('foobasr' , 'oo|ar','') ----> fbasr
select regexp_replace('foobasr' , 'oo|ba','') --->fsr
ps:正则表达式中的 | 竖线代表的是:'或'的意思,其中有一个为true,那整体就是true regexp_extract(正则表达式的解析函数)
- 语法:regexp_extract(string subject, string pattern, int index)
- 返回值:string
- 说明:将字符串subject 按照pattern正则表达式的规则拆分,返回index指定的字符
举例: select regexp_extract('foothebar','foo(.*?)(bar)' ,0) ----> foo select regexp_extract('foothebar','foo(.*?)(bar)' ,1)----> the select regexp_extract('foothebar','foo(.*?)(bar)' ,2) ---> bar 上述代码,会将字符串 foothebar 拆分成 foor, the,bar; 对应的index 索引分别是:0,1,2
get_json_object(json解析函数)
- 语法:get_json_object(string json_string, string path)
- 返回值:string
- 说明:解析json 的字符串json_string, 返回path指定的内容,如果输入的json字符串无效,那么返回null
split(分割字符串函数)
- 语法:split(string str, string pat)
- 返回值:array
- 说明:按照pat分隔符分割 str, 返回分割后的字符串数组
select split('adgncf','n') --> ["adg","cf"] explode(炸裂函数)
- 语法:lateral view explode(split(string str, string pat)) tmp as column1
- 返回值:string
- 说明:按照pat分隔符分割 str,并将数组中的内容炸裂成多行字符串
举例:
select student_score from test lateral_view explode(split(student_score,',')) sc as student_score posexplode(炸裂函数,带有下角标pos)
- 语法:lateral view posexplode(split(string str, string pat)) tmp as pos,item
- 返回值:string
- 说明:按照pat分隔符分割 str,并将数组中的内容炸裂成多行字符串(炸裂带有下角标pos)
举例:
select student_name,
student_score
from test
lateral_view posexplode(split(student_name,',')) sn as student_name_index, student_name
laretal view posexplode(split(student_score,',')) sc as student_score_index,student_score
where student_name_index = student_score_index ; ps: 炸裂函数的具体使用场景见文章:
HiveSQL题——数据炸裂和数据合并-CSDN博客文章浏览阅读711次,点赞17次,收藏11次。HiveSQL题——数据炸裂和数据合并https://blog.csdn.net/SHWAITME/article/details/135952216?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
2.5 聚合函数
count(个数统计函数)
- 语法:count(*),count(col)计数
- 返回值:int
- 说明:count(*)会统计包括null值在内的行;
count(expr)返回指定字段的个数(会过滤null值);
count(distinct expr)返回指定字段的去重后个数(会过滤null值) - 举例:select count(user_id) from table;
sum(总和统计函数)
- 语法:sum(col)
- 返回值:double
- 说明:sum(col) 统计某个结果集中col列相加的结果;
sum(distinct col )某个结果集中col列去重后相加的结果 - 举例:select sum(*) from table;
avg(平均值统计函数)
- 语法:avg(col) ,avg(distinct col)
- 返回值:double
- 说明:avg(col)统计某个结果集中col列的平均值;
avg(distinct col)统计某个结果集中col列去重后的平均值 - 举例:select avg(score) from table;
min(最小值统计函数)
- 语法:min(col)
- 返回值:double
- 说明:统计某个结果集中col列的最小值
- 举例:select min(score) from table
max(最大值统计函数)
- 语法:max(col)
- 返回值:double
- 说明:统计某个结果集中col列的最大值
- 举例:select max(score) from table
-- 总结:
1.count(*)操作时会统计null值,count(column)会过滤掉null值;
2.事实上除了count(*)计算,剩余的聚合函数例如: max(column),min(column),avg(column),count(column) 函数会过滤掉null值高级聚合函数
collect_list(多行变一行,不去重)
- 语法:collect_list(col)
- 返回值:array
- 说明:在hive中是把一个key的多个信息收集起来合成一个,不去重
- 举例:select avg(score) from table;
-- 举例:
with tmp as (
select 'a' as test union all
select 'c' as test union all
select 's' as test union all
select 'd' as test
)
select collect_list(test) from tmp;
结果:["c","s","d","a"] ,可以看出:聚合后的数组元素无法保证顺序性collect_set(多行变一行,去重)
- 语法:collect_set(col)
- 返回值:array
- 说明:在hive中是把一个key的多个信息收集起来,去重
- 举例:select avg(score) from table;
-- 举例:
with tmp as (
select 'a' as test union all
select 'c' as test union all
select 'a' as test union all
select 'd' as test
)
select collect_set(test) from tmp;
结果:["a","c","d"]ps: 聚合函数的具体使用场景见文章:
2.6 开窗函数
聚合函数
- 聚合函数分类: count()、sum()、min()、max()、avg()
- 语法:聚合函数() over( partition by column order by column rows / range between………………)
ps: 聚合函数的具体使用场景见文章:
前后函数
-
lag
-- 取得column列前边的第n行数据,如果存在则返回,如果不存在,返回默认值default
lag(column,n,default) over(partition by order by)-
lead
-- 取得column列后边的第n行数据,如果存在则返回,如果不存在,返回默认值default
lead(column,n,default) over(partition by order by),ps: 前后函数的具体使用场景见文章:
头尾函数
-
first_value
---当前窗口column列的第一个数值,如果有null值,则跳过
first_value(column,true) over (partition by ..order by.. 窗口子句)
---当前窗口column列的第一个数值,如果有null值,不跳过
first_value(column,false) over (partition by ..order by.. 窗口子句)
-
last_value
--- 当前窗口column列的最后一个数值,如果有null值,则跳过
last_value(column,true) over (partition by ..order by.. 窗口子句)
--- 当前窗口column列的最后一个数值,如果有null值,不跳过
last_value(column,false) over (partition by ..order by.. 窗口子句) 排名函数
row_number() over(partition by .. order by .. ) 顺序排序(行号)——1、2、3
rank() over(partition by .. order by .. ) 并列排序,跳过重复序号——1、1、3
dense_rank() over(partition by .. order by .. ) 并列排序,不跳过重复序号——1、1、2ps:排序函数的具体使用场景见文章:
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/SHWAITME/article/details/135986201
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_65441.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!