本文介绍: 四、使用@EventListener注解的方式来监听发布事件。
一、新建一个实体对象
package com.example.demo.model;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class UserModel {
//用户名
private String name;
//密码
private String password;
}
二、新建一个Service以及控制器
UserService .java
package com.example.demo.service;
import com.example.demo.model.UserModel;
public interface UserService {
/**
* 用户注册
* @param userModel
*/
void register(UserModel userModel);
}
UserServiceImpl.java
package com.example.demo.service.impl;
import com.example.demo.event.UserRegisterEvent;
import com.example.demo.model.UserModel;
import com.example.demo.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void register(UserModel userModel) {
userModel.setName("小明");
userModel.setPassword("123456");
applicationContext.publishEvent(new UserRegisterEvent(this,userModel));
}
}
TestController.java
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping(value = "/test2")
public Object test2() {
UserModel userModel = new UserModel();
userService.register(userModel);
return "success";
}三、新建一个UserRegisterEvent类用于发布事件
package com.example.demo.event;
import com.example.demo.model.UserModel;
import lombok.Getter;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
@Getter
public class UserRegisterEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private UserModel userModel;
public UserRegisterEvent(Object source, UserModel userModel) {
super(source);
this.userModel = userModel;
}
}
四、使用@EventListener注解的方式来监听发布事件
package com.example.demo.listener;
import com.example.demo.event.UserRegisterEvent;
import com.example.demo.model.UserModel;
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class AnnotationRegisterListener {
@EventListener
public void register(UserRegisterEvent userRegisterEvent)
{
//获取注册用户对象
UserModel user = userRegisterEvent.getUserModel();
//../省略逻辑
//输出注册用户信息
System.out.println("@EventListener注册信息,用户名:"+user.getName()+",密码:"+user.getPassword());
}
}
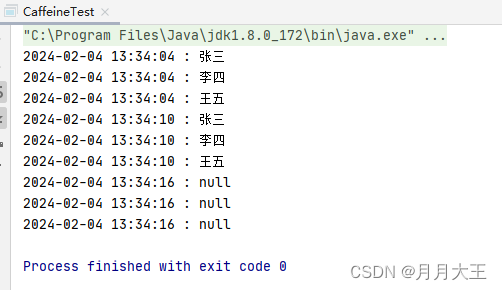
运行结果如下
@EventListener注册信息,用户名:小明,密码:123456五、通过实现ApplicationListener来实现
package com.example.demo.listener;
import com.example.demo.event.UserRegisterEvent;
import com.example.demo.model.UserModel;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class RegisterListener implements ApplicationListener<UserRegisterEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(UserRegisterEvent event) {
UserModel user = event.getUserModel();
//输出注册用户信息
System.out.println("@RegisterListener注册信息,用户名:"+user.getName()+",密码:"+user.getPassword());
}
}
运行结果如下
@RegisterListener注册信息,用户名:小明,密码:123456六、使用SmartApplicationListener实现有序事件
getOrder方法返回的约小约靠前
package com.example.demo.listener;
import com.example.demo.event.UserRegisterEvent;
import com.example.demo.model.UserModel;
import com.example.demo.service.UserService;
import com.example.demo.service.impl.UserServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.event.SmartApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 实现有序监听
*/
@Component
public class UserRegisterListener implements SmartApplicationListener {
/**
* 该方法返回true&supportsSourceType同样返回true时,才会调用该监听内的onApplicationEvent方法
*
* @param eventType 接收到的监听事件类型
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean supportsEventType(Class<? extends ApplicationEvent> eventType) {
//System.out.println(eventType);
//System.out.println(UserRegisterEvent.class);
System.out.println("supportsEventType:" + (eventType == UserRegisterEvent.class));
return eventType == UserRegisterEvent.class;
}
/**
* 该方法返回true&supportsEventType同样返回true时,才会调用该监听内的onApplicationEvent方法
*
* @param aClass
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean supportsSourceType(Class<?> aClass) {
//只有在UserService内发布的UserRegisterEvent事件时才会执行下面逻辑
System.out.println("supportsSourceType:" + (aClass == UserServiceImpl.class));
return aClass == UserServiceImpl.class;
}
/**
* supportsEventType & supportsSourceType 两个方法返回true时调用该方法执行业务逻辑
*
* @param applicationEvent 具体监听实例,这里是UserRegisterEvent
*/
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent applicationEvent) {
/*try {
Thread.sleep(3000);//静静的沉睡3秒钟
}catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}*/
//转换事件类型
UserRegisterEvent userRegisterEvent = (UserRegisterEvent) applicationEvent;
//获取注册用户对象信息
UserModel user = userRegisterEvent.getUserModel();
System.out.println("UserRegisterListener2用户:"+user.getName()+",注册成功,发送邮件通知。");
}
/**
* 同步情况下监听执行的顺序
* @return
*/
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 1;
}
}
输出结果如下
UserRegisterListener2用户:小明,注册成功,发送邮件通知。七、使用异步事件,增加系统效率
onApplicationEvent.java类,onApplicationEvent方法上新增@Async注解即可
package com.example.demo.listener;
import org.springframework.aop.interceptor.AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncConfigurer;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class ListenerAsyncConfiguration implements AsyncConfigurer {
/**
* 获取异步线程池执行对象
* @return
*/
@Override
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
//使用Spring内置线程池任务对象
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
//设置线程池参数
taskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(5);
taskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(10);
taskExecutor.setQueueCapacity(25);
taskExecutor.initialize();
return taskExecutor;
}
@Override
public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
return null;
}
}
package com.example.demo.listener;
import com.example.demo.event.UserRegisterEvent;
import com.example.demo.model.UserModel;
import com.example.demo.service.UserService;
import com.example.demo.service.impl.UserServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.event.SmartApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 实现有序监听
*/
@Component
public class UserRegisterListener implements SmartApplicationListener {
/**
* 该方法返回true&supportsSourceType同样返回true时,才会调用该监听内的onApplicationEvent方法
*
* @param eventType 接收到的监听事件类型
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean supportsEventType(Class<? extends ApplicationEvent> eventType) {
//System.out.println(eventType);
//System.out.println(UserRegisterEvent.class);
System.out.println("supportsEventType:" + (eventType == UserRegisterEvent.class));
return eventType == UserRegisterEvent.class;
}
/**
* 该方法返回true&supportsEventType同样返回true时,才会调用该监听内的onApplicationEvent方法
*
* @param aClass
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean supportsSourceType(Class<?> aClass) {
//只有在UserService内发布的UserRegisterEvent事件时才会执行下面逻辑
System.out.println("supportsSourceType:" + (aClass == UserServiceImpl.class));
return aClass == UserServiceImpl.class;
}
/**
* supportsEventType & supportsSourceType 两个方法返回true时调用该方法执行业务逻辑
*
* @param applicationEvent 具体监听实例,这里是UserRegisterEvent
*/
@Async
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent applicationEvent) {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);//静静的沉睡3秒钟
}catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
//转换事件类型
UserRegisterEvent userRegisterEvent = (UserRegisterEvent) applicationEvent;
//获取注册用户对象信息
UserModel user = userRegisterEvent.getUserModel();
System.out.println("延时3秒后UserRegisterListener用户:"+user.getName()+",注册成功,发送邮件通知。");
}
/**
* 同步情况下监听执行的顺序
* @return
*/
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 1;
}
}
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27787701/article/details/135976252
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_65915.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。