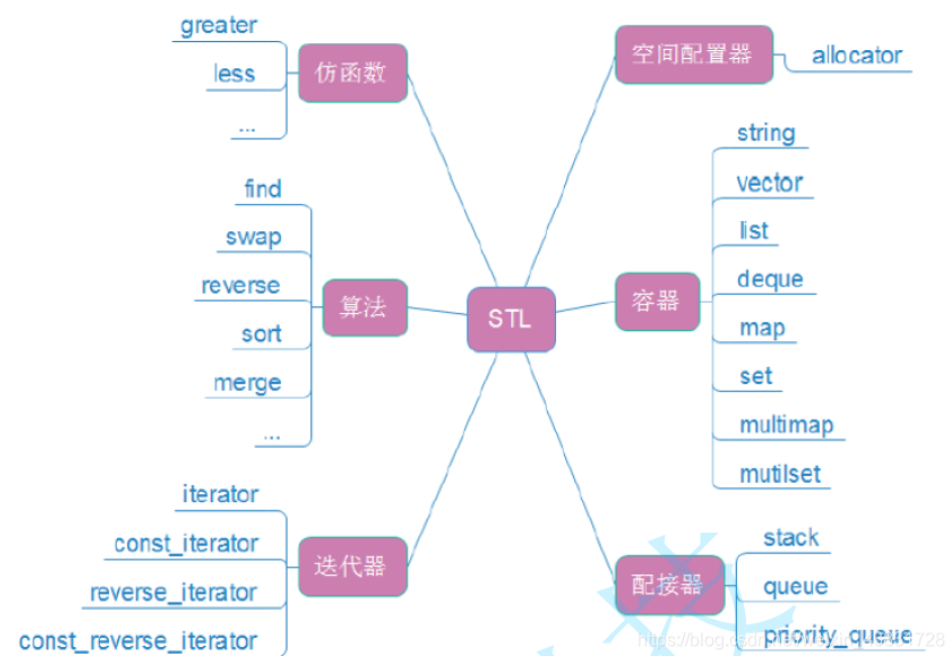
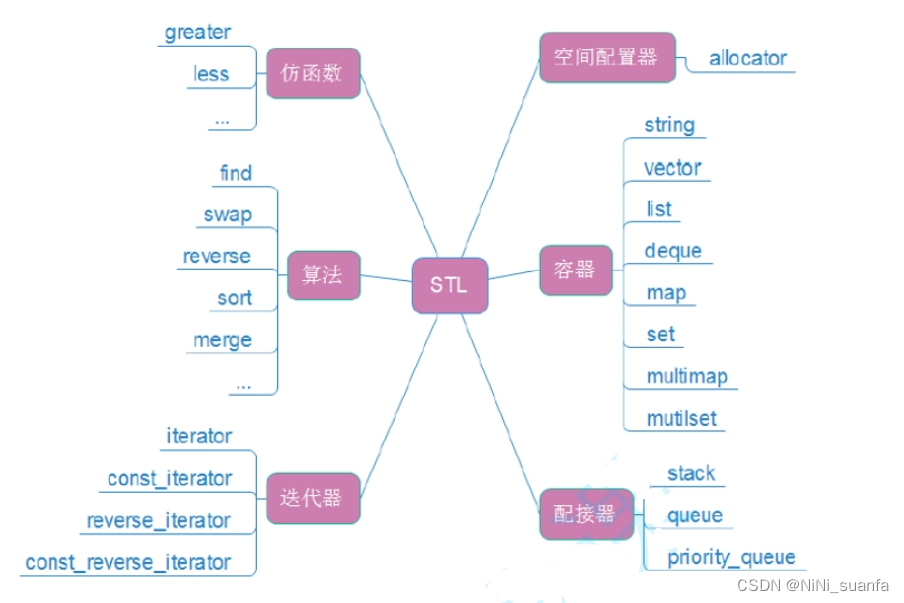
近来看了看《STL源码剖析》中的空间配置器,尝试着读了一下,觉得模板还是强大的,同时对于allocator的函数有了进一步的认识。
#if 0
#include<memory>
//alloctor 的必要接口
allocator::valuetype
allocator::pointer
allocator::const_pointer
allocator::reference
allocator::const_reference
allocator::size_type
allocator::difference_type
allocator::rebind
allocator::allocactor() //default constructor
allocator::allocator(const allocator&) //copy constructor
template <class U>allocator::allocator(const allocator<U>&) //泛化的 copy constructor
allocator::~allocator//default constructor
pointer allocator::address(reference x) const//返回某个对象的地址。a.address(x) const 等同于&x
const_pointer allocator::address(const_reference x) const//返回某个const 对象的地址
pointer allocator::allocate(size_type n,const void* = 0) //分配空间,存n个对象。第二个参数是提示,实现上可能会利用它来增进区域性,可忽略
void allocator::deallocate(point p,size_type n) //归还当前分配的空间
size_type allocator::max_size() const //返回可成功分配的最大量
void allocator::construct(point p,const T& x) //等同于new
void allocator::destroy(point p) //等同于p->~T()
#endif
//设计一个简单的空间配置器 allocator
//file:steem_alloc.h 自己的头文件
#ifndef _STEEMALLOC_
#define _STEEMALLOC_
#include<new>
#include<cstddef>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<climits>
#include<iostream>
namespace steem
{
template <class T>
inline T* _allocate(ptrdiff_t size, T*)
{
set_new_handler(0);
T* tmp = (T*)(::operator new((size_t)(size * sizeof(T))));
if (tmp == 0)
{
cerr << "out of memory" << endl;
exit(1);
}
return tmp;
}
template <class T>
inline void _deallocate(T* buffer)
{
::operator delete(buffer);
}
template <class T1,class T2>
inline void _construct(T1* p, const T2& value)
{
new(p) T1(value);
}
template <class T>
inline void _destroy(T* ptr)
{
ptr->~T();
}
template <class T>
class allocator
{
public:
typedef T value_type;
typedef T* pointer;
typedef const T* const_pointer;
typedef T& reference;
typedef const T& const_reference;
typedef ptrdiff_t defference_type;
//rebind allocator of type U
template <class U>
struct rebind
{
typedef alloactor<U> other;
};
pointer allocate(size_type n, const void* hint = 0)
{
return _allocate(((difference_type)n, (pointer)0));
}
void deallocate(point p, size_type n) { _deallocate(p); }
void construct(pointer p, const T& value)
{
_construct(p, value);
}
void destroy(point p) { _destroy(p); }
pointer address(reference x) { return (pointer)&x; }
const_pointer const_address(const_reference x)
{
return (const_pointer)&x;
}
size_type max_size() const
{
return size_type(UINT_MAX / sizeof(T));
}
};
}
#endif //STEMMALLOC
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//main 函数中
int main_t1()
{
int ia[5] = { 0,1,2,3,4 };
unsigned int i;
vector<int, steem::allocator<int> > iv(ia, ia + 5);
for (i = 0; i < iv.size(); i++)
{
cout << iv[i] << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_34161171/article/details/134697041
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_9555.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
主题授权提示:请在后台主题设置-主题授权-激活主题的正版授权,授权购买:RiTheme官网
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。